Tongue cancer
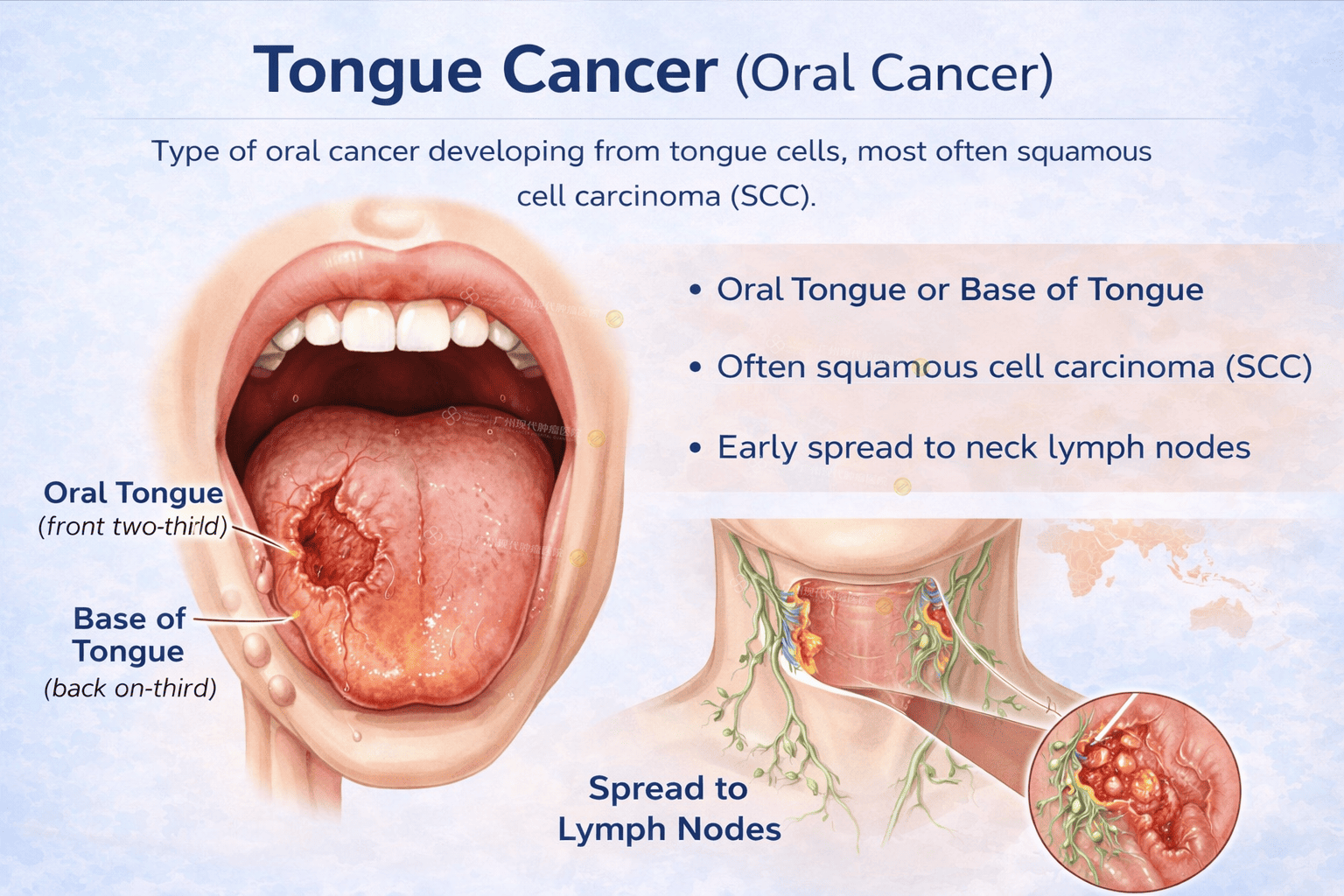
Tongue cancer is a type of oral cancer that develops from the cells of the tongue, most commonly squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). It can arise on the front two-thirds of the tongue (oral tongue) or the base of the tongue (oropharyngeal tongue).
Tongue cancer tends to be aggressive because the tongue has a rich blood and lymphatic supply, allowing cancer cells to spread early to neck lymph nodes if not detected promptly.
Types
Tongue cancer is classified by location and histology.
By Location
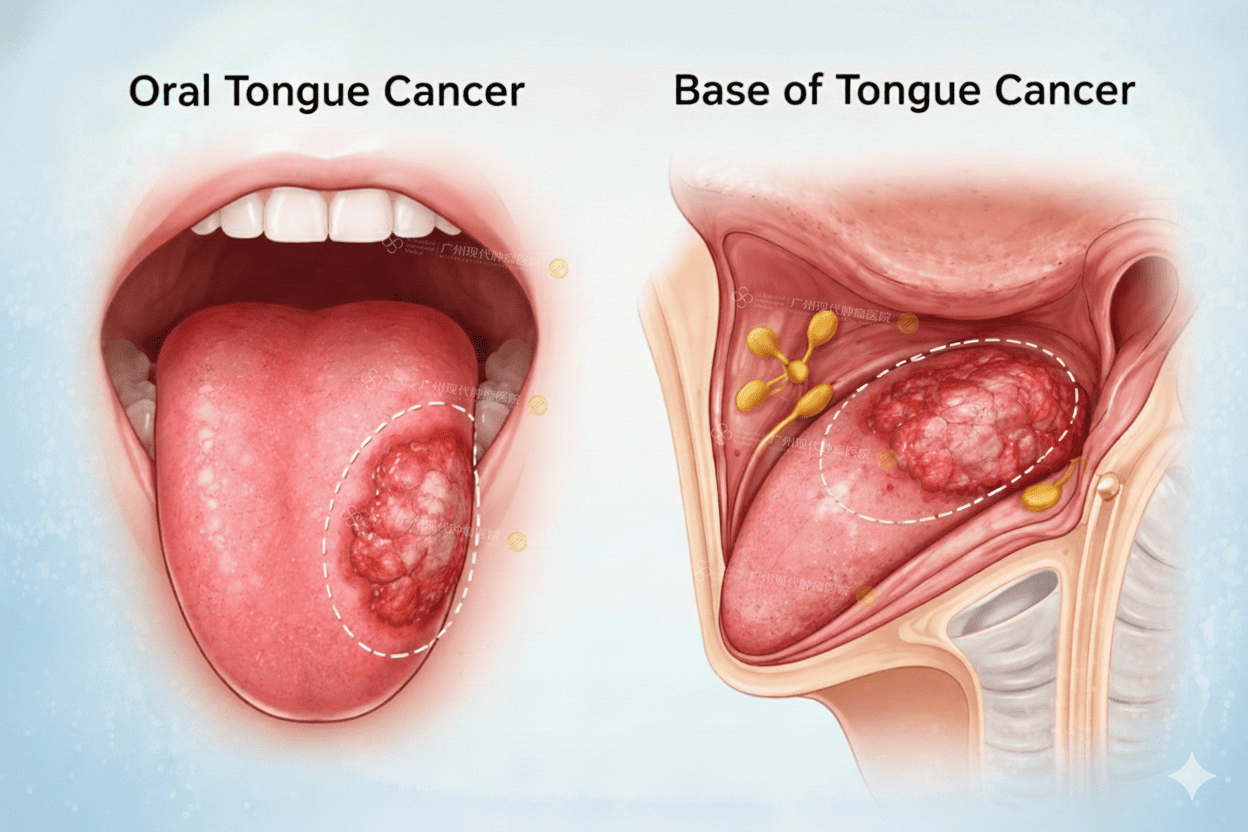
Oral tongue cancer
Front 2/3 of the tongue
More visible, often detected earlier
Base of tongue cancer
Back 1/3 of the tongue (part of oropharynx)
Often linked to HPV infection
Diagnosed later due to subtle symptoms
By Histology
Squamous cell carcinoma (≈90%)
Verrucous carcinoma (slow-growing variant)
Rare types: adenocarcinoma, lymphoma, melanoma
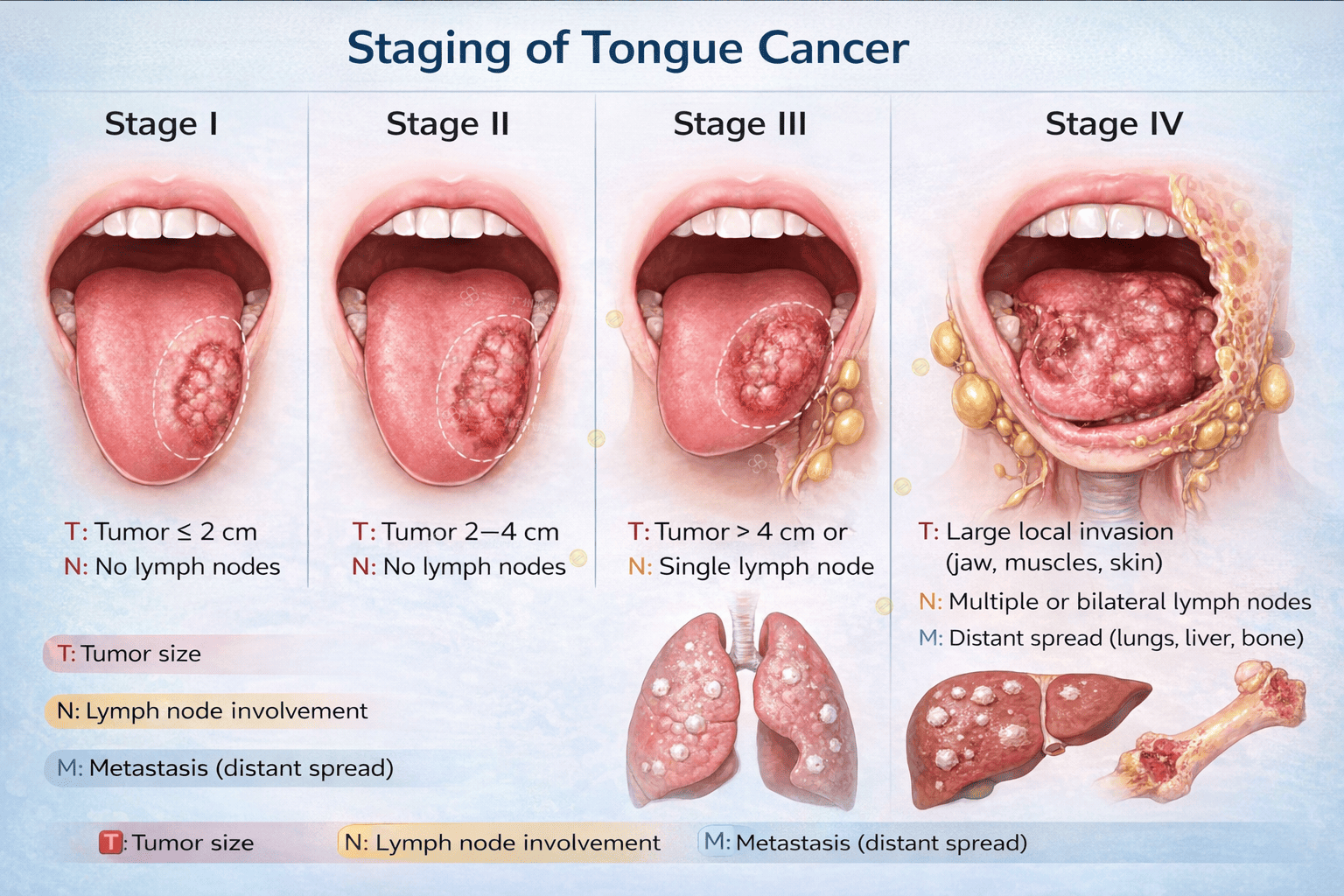
Stages
Tongue cancer staging depends on tumor size (T), lymph node involvement (N), and metastasis (M).
Stage I:Tumor ≤2 cm, no lymph nodes
Stage II:Tumor 2–4 cm, no lymph nodes
Stage III:Tumor >4 cm or single lymph node involved
Stage IV:
Large local invasion (jaw, muscles, skin)
Multiple or bilateral lymph nodes
Distant spread (lungs, liver, bone)
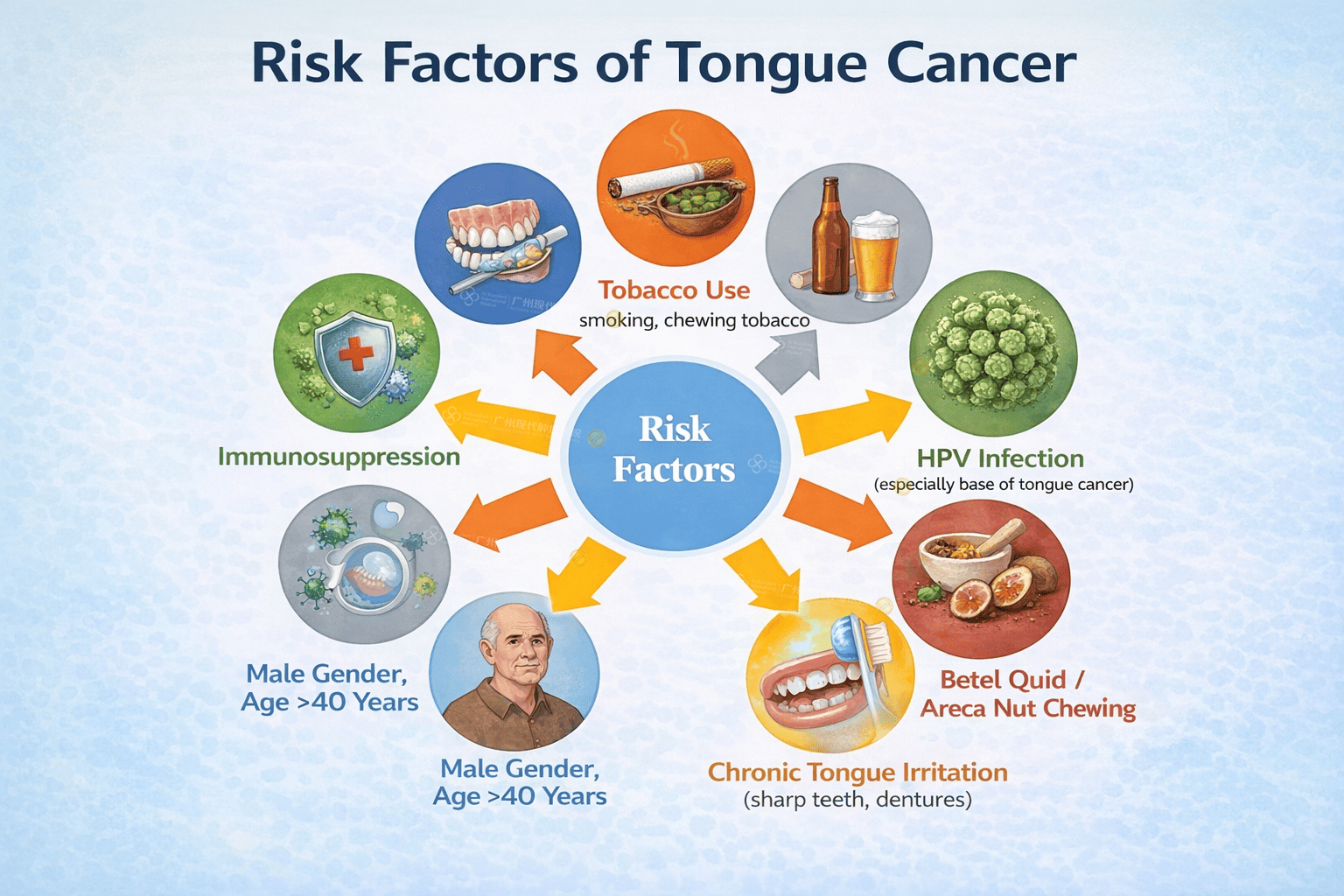
Risk Factors
Tobacco use (smoking, chewing tobacco)
Alcohol consumption (synergistic with smoking)
HPV infection (especially base of tongue cancer)
Betel quid / areca nut chewing
Poor oral hygiene
Chronic tongue irritation (sharp teeth, dentures)
Male gender, age >40 years
Immunosuppression
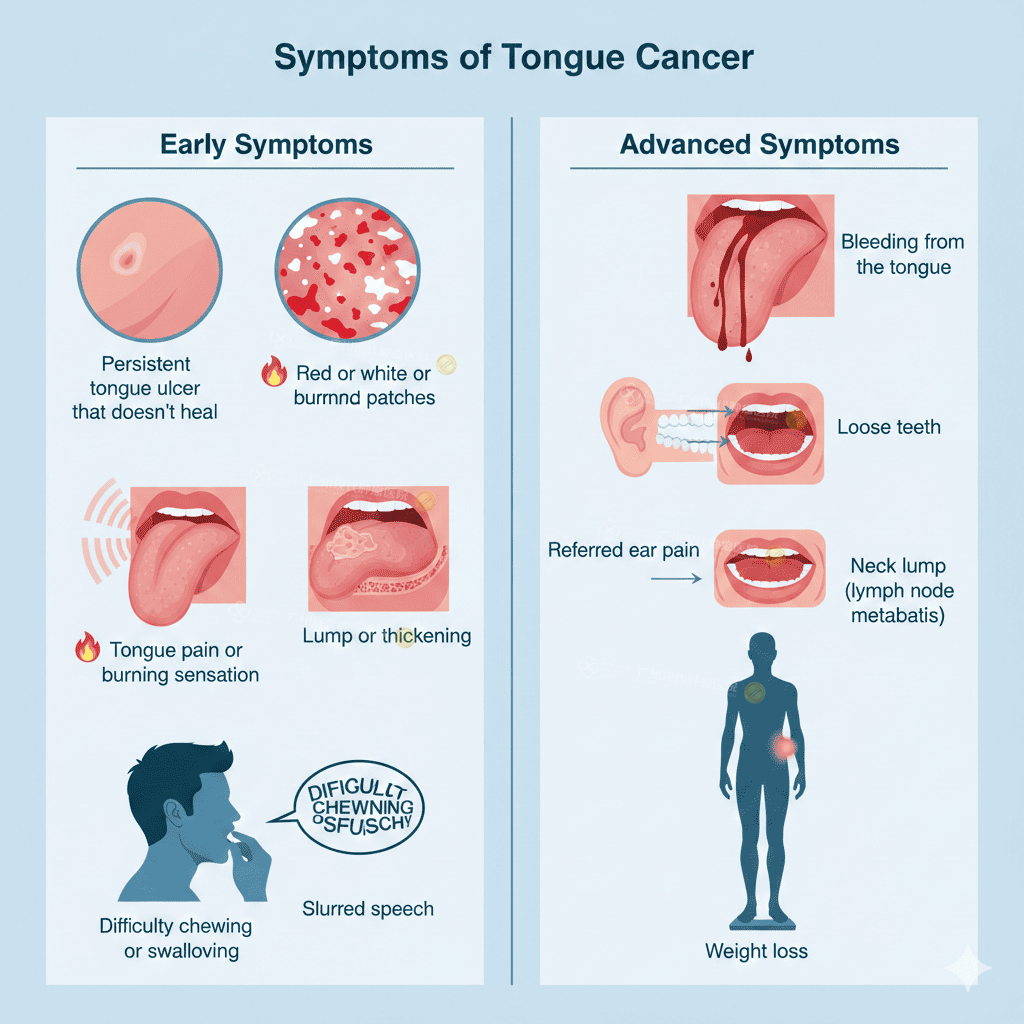
Symptoms
Early symptoms are often mild and ignored.
Common symptoms
Persistent tongue ulcer that doesn’t heal
Red (erythroplakia) or white patches (leukoplakia)
Tongue pain or burning sensation
Lump or thickening in the tongue
Difficulty chewing or swallowing
Slurred speech
Advanced symptoms
Bleeding from the tongue
Referred ear pain
Loose teeth
Neck lump (lymph node metastasis)
Weight loss
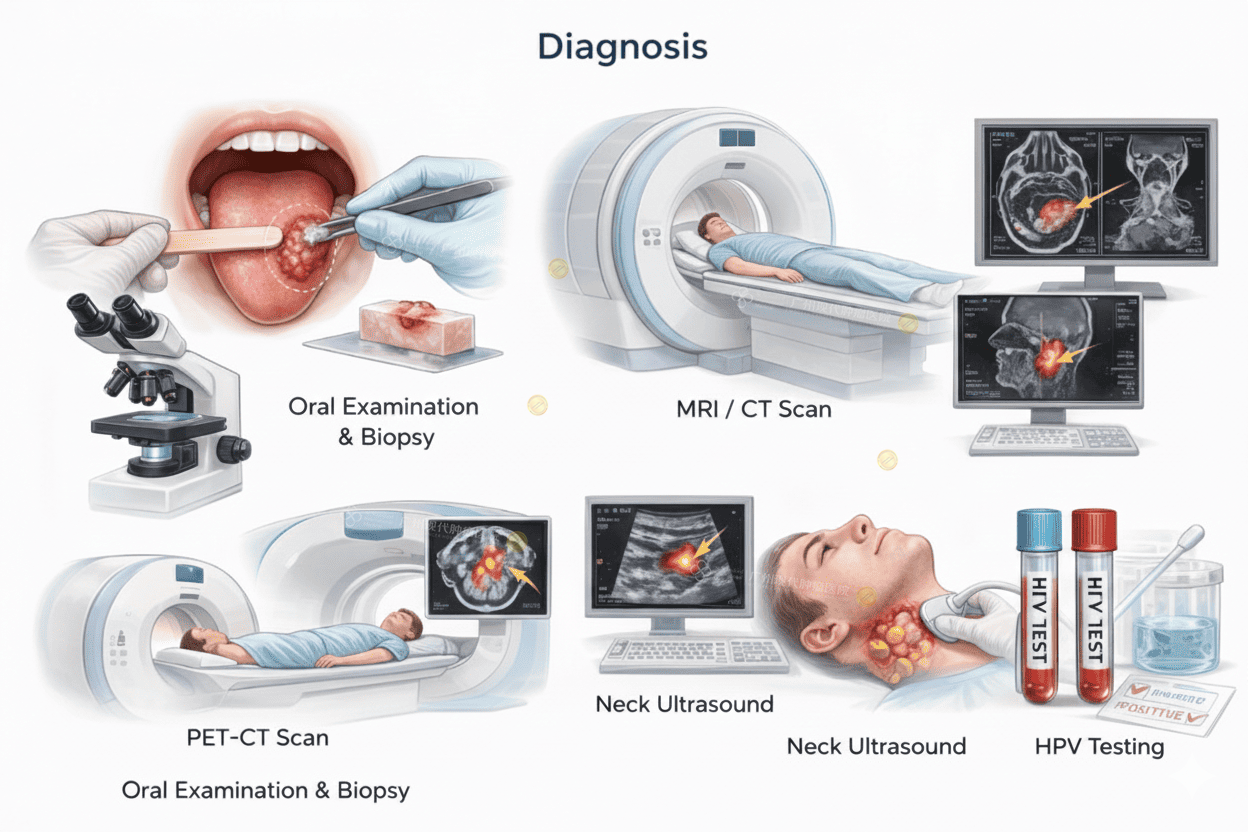
Diagnosis
Diagnosis requires both clinical evaluation and tissue confirmation.
Oral examination
Biopsy (gold standard)
Imaging
MRI / CT scan → tumor extent
PET-CT → metastasis
Neck ultrasound for lymph nodes
HPV testing (especially for base of tongue tumors)
Q1: Is tongue cancer curable?
Yes — especially when detected early.
Q2: Is tongue cancer painful?
Early stages may be painless; pain usually appears later.
Q3: Can young people get tongue cancer?
Yes, especially HPV-related base of tongue cancers.
Q4: Does tongue cancer spread fast?
It can spread early to neck lymph nodes due to rich lymphatics.
Q5: How to reduce risk?
Stop smoking, limit alcohol, maintain oral hygiene, treat HPV, and get regular oral checks.